NXP MIMXRT1160-EVK
Overview
The dual core i.MX RT1160 runs on the Cortex-M7 core at 600 MHz and on the Cortex-M4 at 240 MHz. The i.MX RT1160 MCU offers support over a wide temperature range and is qualified for consumer, industrial and automotive markets.
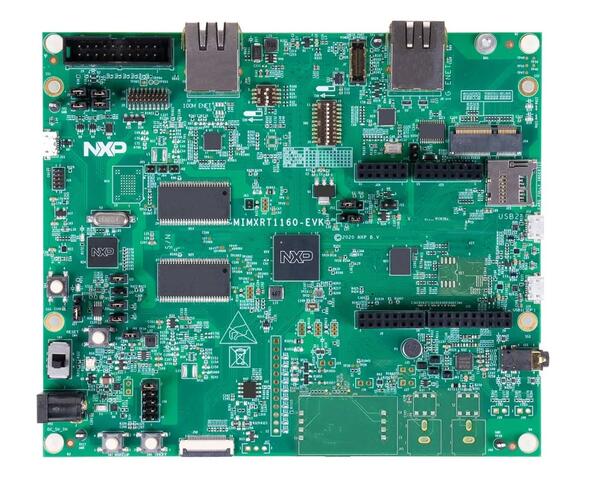
Hardware
MIMXRT1166DVM6A MCU
600MHz Cortex-M7 & 240Mhz Cortex-M4
2MB SRAM with 512KB of TCM for Cortex-M7 and 256KB of TCM for Cortex-M4
Memory
512 Mbit SDRAM
128 Mbit QSPI Flash
512 Mbit Octal Flash
TF socket for SD card
Display
MIPI LCD connector
Ethernet
10/100 Mbit/s Ethernet PHY
10/100/1000 Mbit/s Ethernet PHY
USB
USB 2.0 OTG connector
USB 2.0 host connector
Audio
3.5 mm audio stereo headphone jack
Board-mounted microphone
Left and right speaker out connectors
Power
5 V DC jack
Debug
JTAG 20-pin connector
OpenSDA with DAPLink
Sensor
MIPI camera sensor connector
Expansion port
Arduino interface
CAN bus connector
For more information about the MIMXRT1160 SoC and MIMXRT1160-EVK board, see these references:
External Memory
This platform has the following external memories:
Device |
Controller |
Status |
|---|---|---|
W9825G6KH |
SEMC |
Enabled via device configuration data block, which sets up SEMC at boot time |
IS25WP128 |
FLEXSPI |
Enabled via flash configurationn block, which sets up FLEXSPI at boot time. |
Supported Features
The mimxrt1160_evk board configuration supports the hardware features listed below. For additional features not yet supported, please also refer to the NXP MIMXRT1170-EVK/EVKB , which is the superset board in NXP’s i.MX RT11xx family. NXP prioritizes enabling the superset board with NXP’s Full Platform Support for Zephyr. Therefore, the mimxrt1170_evk board may have additional features already supported, which can also be re-used on this mimxrt1160_evk board:
Interface |
Controller |
Driver/Component |
|---|---|---|
NVIC |
on-chip |
nested vector interrupt controller |
SYSTICK |
on-chip |
systick |
GPIO |
on-chip |
gpio |
COUNTER |
on-chip |
counter |
UART |
on-chip |
serial port-polling; serial port-interrupt |
SPI |
on-chip |
spi |
I2C |
on-chip |
i2c |
ADC |
on-chip |
adc |
CAN |
on-chip |
flexcan |
WATCHDOG |
on-chip |
watchdog |
PWM |
on-chip |
pwm |
DMA |
on-chip |
dma |
GPT |
on-chip |
gpt |
USB |
on-chip |
USB Device |
HWINFO |
on-chip |
Unique device serial number |
CAAM RNG |
on-chip |
entropy |
FLEXSPI |
on-chip |
flash programming |
PIT |
on-chip |
pit |
DISPLAY |
on-chip |
eLCDIF; MIPI-DSI. Tested with NXP RK055HDMIPI4M MIPI Display, NXP RK055HDMIPI4MA0 MIPI Display, and NXP G1120B0MIPI MIPI Display shields |
The default configuration can be found in the defconfig file: boards/nxp/mimxrt1160_evk/mimxrt1160_evk_mimxrt1166_cm7_defconfig
Other hardware features are not currently supported by the port.
Connections and I/Os
The MIMXRT1160 SoC has six pairs of pinmux/gpio controllers.
Name |
Function |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
WAKEUP |
GPIO |
SW7 |
GPIO_AD_04 |
GPIO |
LED |
GPIO_AD_24 |
LPUART1_TX |
UART Console |
GPIO_AD_25 |
LPUART1_RX |
UART Console |
GPIO_LPSR_00 |
CAN3_TX |
flexcan |
GPIO_LPSR_01 |
CAN3_RX |
flexcan |
GPIO_AD_29 |
SPI1_CS0 |
spi |
GPIO_AD_28 |
SPI1_CLK |
spi |
GPIO_AD_30 |
SPI1_SDO |
spi |
GPIO_AD_31 |
SPI1_SDI |
spi |
GPIO_AD_08 |
LPI2C1_SCL |
i2c |
GPIO_AD_09 |
LPI2C1_SDA |
i2c |
GPIO_LPSR_05 |
LPI2C5_SCL |
i2c |
GPIO_LPSR_04 |
LPI2C5_SDA |
i2c |
GPIO_AD_04 |
FLEXPWM1_PWM2 |
pwm |
Dual Core samples
Core |
Boot Address |
Comment |
|---|---|---|
Cortex M7 |
0x30000000[630K] |
primary core |
Cortex M4 |
0x20020000[96k] |
boots from OCRAM |
Memory |
Address[Size] |
Comment |
|---|---|---|
flexspi1 |
0x30000000[16M] |
Cortex M7 flash |
sdram0 |
0x80030000[64M] |
Cortex M7 ram |
ocram |
0x20020000[512K] |
Cortex M4 “flash” |
sram1 |
0x20000000[128K] |
Cortex M4 ram |
ocram2 |
0x200C0000[512K] |
Mailbox/shared memory |
Only the first 16K of ocram2 has the correct MPU region attributes set to be used as shared memory
System Clock
The MIMXRT1160 SoC is configured to use SysTick as the system clock source, running at 600MHz. When targeting the M4 core, SysTick will also be used, running at 240MHz
When power management is enabled, the 32 KHz low frequency oscillator on the board will be used as a source for the GPT timer to generate a system clock. This clock enables lower power states, at the cost of reduced resolution
Serial Port
The MIMXRT1160 SoC has 12 UARTs. One is configured for the console and the remaining are not used.
Programming and Debugging
Build and flash applications as usual (see Building an Application and Run an Application for more details).
Building a Dual-Core Image
Dual core samples load the M4 core image from flash into the shared ocram
region. The M7 core then sets the M4 boot address to this region. The only
sample currently enabled for dual core builds is the openamp sample.
To flash a dual core sample, the M4 image must be flashed first, so that it is
written to flash. Then, the M7 image must be flashed. The openamp sysbuild
sample will do this automatically by setting the image order.
The secondary core can be debugged normally in single core builds
(where the target is mimxrt1160_evk/mimxrt1166/cm4). For dual core builds, the
secondary core should be placed into a loop, then a debugger can be attached
(see AN13264, section 4.2.3 for more information)
Configuring a Debug Probe
A debug probe is used for both flashing and debugging the board. This board is configured by default to use the OpenSDA DAPLink Onboard Debug Probe, however the pyOCD Debug Host Tools do not yet support programming the external flashes on this board so you must reconfigure the board for one of the following debug probes instead.
Using J-Link
Install the J-Link Debug Host Tools and make sure they are in your search path.
There are two options: the onboard debug circuit can be updated with Segger J-Link firmware, or J-Link External Debug Probe can be attached to the EVK. See Using J-Link with MIMXRT1160-EVK or MIMXRT1170-EVK for more details.
Using LinkServer
Install the LinkServer Debug Host Tools and make sure they are in your
search path. LinkServer works with the CMSIS-DAP firmware include in LinkServer
install. Please follow the LPCScrypt\docs\Debug_Probe_Firmware_Programming.pdf
for more details.
Linkserver is the default runner. You may also se the -r linkserver option
with West to use the LinkServer runner.
Configuring a Console
Regardless of your choice in debug probe, we will use the OpenSDA microcontroller as a usb-to-serial adapter for the serial console. Check that jumpers J5 and J8 are on (they are on by default when boards ship from the factory) to connect UART signals to the OpenSDA microcontroller.
Connect a USB cable from your PC to J11.
Use the following settings with your serial terminal of choice (minicom, putty, etc.):
Speed: 115200
Data: 8 bits
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flashing
Here is an example for the Hello World application.
Before power on the board, make sure SW1 is set to 0001b
# From the root of the zephyr repository
west build -b mimxrt1160_evk/mimxrt1166/cm7 samples/hello_world
west flash
Power off the board, and change SW1 to 0010b. Then power on the board and open a serial terminal, reset the board (press the SW4 button), and you should see the following message in the terminal:
***** Booting Zephyr OS v2.6.0-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxxx *****
Hello World! mimxrt1160_evk
Debugging
Here is an example for the Hello World application.
# From the root of the zephyr repository
west build -b mimxrt1160_evk/mimxrt1166/cm7 samples/hello_world
west debug
Open a serial terminal, step through the application in your debugger, and you should see the following message in the terminal:
***** Booting Zephyr OS v2.4.0-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxxx *****
Hello World! mimxrt1160_evk
