Bootloaders and DFU
Depending on the device, you need to use different bootloader and DFU solutions:
For the nRF54H Series, use Software Updates for Internet of Things (SUIT). The SUIT procedure is the only supported bootloader and Device Firmware Update (DFU) procedure for this device.
For the remaining Nordic Semiconductor devices, use MCUboot and nRF Secure Immutable Bootloader (NSIB).
See the following diagram and table for further comparison.
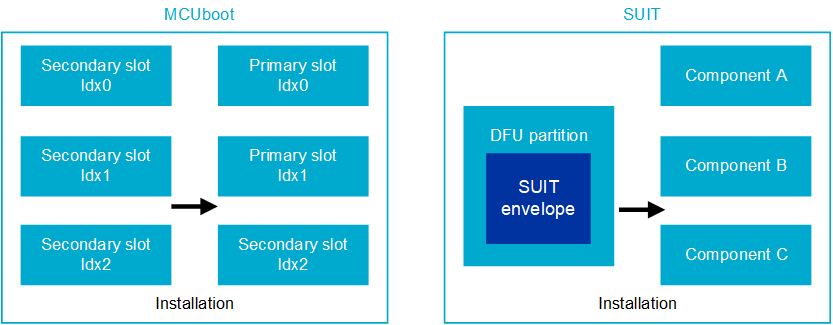
MCUboot, SUIT, and nRF Secure Immutable Bootloader architecture comparison
Characteristic |
MCUboot |
SUIT |
nRF Secure Immutable Bootloader |
|---|---|---|---|
Primary function |
Bootloader and DFU |
Flexible, script-based DFU system |
Secure Immutable Bootloader |
Customization |
Built by users; partitions customized with Kconfig options and DTS. Kconfig and DTS configurable with multi-image builds or sysbuild. Becomes static post-compilation. |
SDFW provided by Nordic, delivered in binary form. Customizable with manifests and configuration. |
Limited; focused on initial boot security. |
Slot management |
Symmetrical primary and secondary slot style. Primary slot is where the system is executed from (by default). Secondary slot is the destination for the DFU (by default). |
Single DFU partition; components act as slots. The DFU partition size can be located anywhere in the nonvolatile memory, accessible in the application core. Information about the location of the DFU is not hardcoded in the SDFW and can be changed between updates. |
Not applicable for firmware updates. |
Slot characteristics |
Equal primary and secondary slot sizes lead to high memory overhead. |
Single DFU partition with customizable component sizes. |
Highly efficient due to immutable design. |
Slot definition |
Static definition; challenging to change post-deployment. |
Technical possibility to change component definitions between updates. |
Fixed and immutable; no post-deployment changes. |
Invocation process |
Limited customization through metadata. |
Flexible customization within the manifest (metadata). |
Authenticated firmware execution; no update mechanism post-boot. |
Flash memory layout |
Specific allocations for primary and secondary slots. |
Single DFU partition with flexible component slots. |
OTP regions for provisioned data; specific layout for boot and application partitions. |
To learn more, refer to the following documentation pages:
