Wi-Fi: Promiscuous
The Promiscuous sample demonstrates how to set Promiscuous mode, establish a connection to an Access Point (AP), analyze incoming Wi-Fi® packets, and print packet statistics.
Requirements
The sample supports the following development kits:
Hardware platforms |
PCA |
Board name |
Board target |
Shields |
|---|---|---|---|---|
PCA10143 |
|
|||
PCA10143 |
|
|||
PCA10095 |
|
|
Overview
The sample demonstrates how to configure the nRF70 Series device in Promiscuous mode, and how to connect the Wi-Fi station to a specified access point using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). It analyzes the incoming Wi-Fi packets on a raw socket and prints the packet statistics at a fixed interval.
Configuration
See Configuring and building for information about how to permanently or temporarily change the configuration.
Configuration options
The following sample-specific Kconfig options are used in this sample (located in samples/wifi/promiscuous/Kconfig):
- CONFIG_PROMISCUOUS_SAMPLE_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT_S
(int) Wi-Fi connection timeout in seconds
None
- CONFIG_PROMISCUOUS_SAMPLE_DHCP_TIMEOUT_S
(int) DHCP timeout in seconds
None
- CONFIG_PROMISCUOUS_SAMPLE_RX_THREAD_STACK_SIZE
(int) Thread stack size
This option sets the stack size for the threads used in the sample.
- CONFIG_PROMISCUOUS_SAMPLE_STATS_PRINT_TIMEOUT
(int) Periodic statistics print timeout
This option sets the timeout for periodic statistics print in seconds.
- CONFIG_PROMISCUOUS_SAMPLE_RECV_BUFFER_SIZE
(int) Size of the receive buffer
This option sets the size of the receive buffer in bytes.
You must configure the following Wi-Fi credentials in the prj.conf file:
Wi-Fi static credential options
If you want to configure the credentials statically, set the CONFIG_WIFI_CREDENTIALS_STATIC Kconfig option to y.
Important
Do not use static credentials in production environments.
Other options for statically configuring your Wi-Fi credentials:
CONFIG_WIFI_CREDENTIALS_STATIC- This option enables static Wi-Fi configuration.CONFIG_WIFI_CREDENTIALS_STATIC_SSID- Wi-Fi SSID.CONFIG_WIFI_CREDENTIALS_STATIC_PASSWORD- Wi-Fi password.CONFIG_WIFI_CREDENTIALS_STATIC_TYPE_OPEN- Wi-Fi network uses no password.CONFIG_WIFI_CREDENTIALS_STATIC_TYPE_PSK- Wi-Fi network uses a password and PSK security (default).CONFIG_WIFI_CREDENTIALS_STATIC_TYPE_PSK_SHA256- Wi-Fi network uses a password and PSK-256 security.CONFIG_WIFI_CREDENTIALS_STATIC_TYPE_SAE- Wi-Fi network uses a password and SAE security.
Note
You can also use menuconfig to configure Wi-Fi credentials.
See Interactive Kconfig interfaces in the Zephyr documentation for instructions on how to run menuconfig.
Building and running
This sample can be found under samples/wifi/promiscuous in the nRF Connect SDK folder structure.
When built as firmware image for a board target with the */ns variant, the sample has Cortex-M Security Extensions (CMSE) enabled and separates the firmware between Non-Secure Processing Environment (NSPE) and Secure Processing Environment (SPE).
Because of this, it automatically includes the Trusted Firmware-M (TF-M).
To read more about CMSE, see Processing environments.
To build the sample, follow the instructions in Building an application for your preferred building environment. See also Programming an application for programming steps and Testing and optimization for general information about testing and debugging in the nRF Connect SDK.
Note
When building repository applications in the SDK repositories, building with sysbuild is enabled by default.
If you work with out-of-tree freestanding applications, you need to manually pass the --sysbuild parameter to every build command or configure west to always use it.
To build for the nRF7002 DK, use the nrf7002dk/nrf5340/cpuapp board target.
The following is an example of the CLI command:
west build -p -b nrf7002dk/nrf5340/cpuapp
Change the board target as given below for the nRF7002 EK.
nrf5340dk/nrf5340/cpuapp -- -DSHIELD=nrf7002ek
Testing
After programming the sample to your development kit, complete the following steps to test it:
Connect the kit to the computer using a USB cable. The kit is assigned a COM port (Windows) or ttyACM device (Linux), which is visible in the Device Manager.
Connect to the kit with a terminal emulator (for example, nRF Connect Serial Terminal). See Testing and optimization for the required settings and steps.
The sample shows the following output:
[00:00:00.433,898] <inf> usb_net: netusb initialized *** Booting nRF Connect SDK v2.6.99-22ce705894ad *** *** Using Zephyr OS v3.6.99-688107b4a1a2 *** [00:00:00.516,448] <inf> net_config: Initializing network [00:00:00.516,448] <inf> net_config: Waiting interface 1 (0x20001020) to be up... [00:00:00.516,601] <inf> net_config: IPv4 address: 192.168.1.99 [00:00:00.516,662] <inf> net_config: Running dhcpv4 client... [00:00:00.519,897] <inf> promiscuous: Promiscuous mode enabled [00:00:00.942,535] <inf> usb_ecm: Set Interface 0 Packet Filter 0x000c not supported [00:00:00.991,516] <inf> usb_ecm: Set Interface 0 Packet Filter 0x000e not supported [00:00:00.993,713] <inf> usb_ecm: Set Interface 0 Packet Filter 0x000e not supported [00:00:00.994,537] <inf> usb_ecm: Set Interface 0 Packet Filter 0x000e not supported [00:00:00.994,995] <inf> usb_ecm: Set Interface 0 Packet Filter 0x000e not supported [00:00:00.996,520] <inf> usb_ecm: Set Interface 0 Packet Filter 0x000e not supported [00:00:03.520,324] <inf> wifi_connect: Static IP address (overridable): 192.168.1.99/255.255.255.0 -> 192.168.1.1 [00:00:03.529,510] <inf> wifi_mgmt_ext: Connection requested [00:00:03.529,541] <inf> wifi_connect: Connection requested [00:00:07.712,585] <inf> wifi_connect: Connected [00:00:07.839,050] <inf> net_dhcpv4: Received: 192.165.100.161 [00:00:07.839,202] <inf> net_config: IPv4 address: 192.165.100.161 [00:00:07.839,202] <inf> net_config: Lease time: 86400 seconds [00:00:07.839,233] <inf> net_config: Subnet: 255.255.0.0 [00:00:07.839,294] <inf> net_config: Router: 192.165.100.68 [00:00:07.839,385] <inf> wifi_connect: DHCP IP address: 192.165.100.161 [00:00:07.842,468] <inf> wifi_connect: ================== [00:00:07.842,498] <inf> wifi_connect: State: COMPLETED [00:00:07.842,529] <inf> wifi_connect: Interface Mode: STATION [00:00:07.842,529] <inf> wifi_connect: Link Mode: WIFI 4 (802.11n/HT) [00:00:07.842,559] <inf> wifi_connect: SSID: AAAAAAAA [00:00:07.842,590] <inf> wifi_connect: BSSID: XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX [00:00:07.842,620] <inf> wifi_connect: Band: 2.4GHz [00:00:07.842,620] <inf> wifi_connect: Channel: 11 [00:00:07.842,620] <inf> wifi_connect: Security: OPEN [00:00:07.842,651] <inf> wifi_connect: MFP: Disable [00:00:07.842,651] <inf> wifi_connect: RSSI: -57 [00:00:07.842,681] <inf> wifi_connect: TWT: Not supported [00:00:07.844,024] <inf> promiscuous: Network capture of Wi-Fi traffic enabled [00:00:07.844,177] <inf> promiscuous: Wi-Fi promiscuous mode RX thread started [00:00:12.869,476] <inf> promiscuous: Management Frames: [00:00:12.869,506] <inf> promiscuous: Beacon Count: 48 [00:00:12.869,506] <inf> promiscuous: Probe Request Count: 0 [00:00:12.869,506] <inf> promiscuous: Probe Response Count: 190 [00:00:12.869,537] <inf> promiscuous: Action Count: 0 [00:00:12.869,537] <inf> promiscuous: Control Frames: [00:00:12.869,567] <inf> promiscuous: ACK Count 0 [00:00:12.869,567] <inf> promiscuous: RTS Count 0 [00:00:12.869,567] <inf> promiscuous: CTS Count 0 [00:00:12.869,567] <inf> promiscuous: Block Ack Count 0 [00:00:12.869,598] <inf> promiscuous: Block Ack Req Count 0 [00:00:12.869,628] <inf> promiscuous: CF End Count 0 [00:00:12.869,628] <inf> promiscuous: Data Frames: [00:00:12.869,628] <inf> promiscuous: Data Count: 9 [00:00:12.869,628] <inf> promiscuous: QoS Data Count: 0 [00:00:12.869,659] <inf> promiscuous: Null Count: 16 [00:00:12.869,659] <inf> promiscuous: QoS Null Count: 8 [00:00:12.869,659] <inf> promiscuous: Unknown Frames: [00:00:12.869,659] <inf> promiscuous: Unknown Management Frame Count: 1 [00:00:12.869,659] <inf> promiscuous: Unknown Control Frame Count: 0 [00:00:12.869,689] <inf> promiscuous: Unknown Data Frame Count: 0 [00:00:12.869,689] <inf> promiscuous: Reserved Frame Count: 0 [00:00:12.869,689] <inf> promiscuous: Unknown Frame Count: 0
Offline net capture
The sample supports the offline net capture feature in Zephyr, see Zephyr net capture for details.
See the Zephyr net capture Linux setup section for instructions on how to set up the Linux host for offline net capture.
Ensure the requirements from Zephyr net capture are met before proceeding.
To enable this feature in this sample, use the overlay-net-capture.conf and overlay-netusb.conf configuration overlay files.
When the offline net capture feature is enabled, incoming IEEE 802.11 packets are routed to the offline storage over the net capture tunnel. These packets can then be analyzed using Wireshark.
Wireshark decode as IEEE 802.11
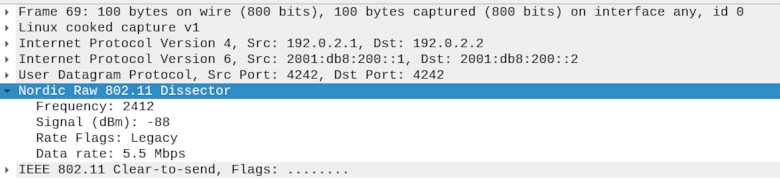
The packets from the device are sent to the host over the net capture tunnel using IP in IP tunneling. The nRF70 Series device sends the IEEE 802.11 packets prepended with a custom metadata over the net capture tunnel to the host. To analyze the packets in Wireshark, the payload of the UDP packets must be dissected as IEEE 802.11 packets.
This support is only available in Wireshark 4.3 (under development - master branch). A custom build of Wireshark from the latest sources is required, see Wireshark Unix Build setup for details. Once the custom build is installed, complete the following steps to dissect the payload of the UDP packets as IEEE 802.11 packets:
Ensure Wireshark is compiled with Lua support, see Wireshark with Lua for details.
Open Wireshark and go to Analyze > Decode As > +, then select UDP.
In the Current column, ensure IEEE 802.11 is available.
If not, then the Wireshark version does not have the support to decode the UDP payload as IEEE 802.11 packets, and you need to build Wireshark from the latest sources.
Copy the following Lua script to a file, for example,
nordic_decode_raw_80211.luafile.-- Create a new dissector local nordic_raw_80211 = Proto("nordic_raw_80211", "Nordic Raw 802.11 dissector") -- No built-in helper to convert a number to a signed char in Lua function toSignedChar(value) if value > 127 then return value - 256 else return value end end local nordic_rate_flags = { NORD_RATE_FLAG_LEGACY = 0, NORD_RATE_FLAG_HT = 1, NORD_RATE_FLAG_VHT = 2, NORD_RATE_FLAG_HE_SU = 3, NORD_RATE_FLAG_HE_ER_SU = 4, NORD_RATE_FLAG_MAX = 5 } function getRateFlags(rate_flags) local rate_flags_str = "" if rate_flags == nordic_rate_flags.NORD_RATE_FLAG_LEGACY then rate_flags_str = "Legacy" elseif rate_flags == nordic_rate_flags.NORD_RATE_FLAG_HT then rate_flags_str = "HT" elseif rate_flags == nordic_rate_flags.NORD_RATE_FLAG_VHT then rate_flags_str = "VHT" elseif rate_flags == nordic_rate_flags.NORD_RATE_FLAG_HE_SU then rate_flags_str = "HE-SU" elseif rate_flags == nordic_rate_flags.NORD_RATE_FLAG_HE_ER_SU then rate_flags_str = "HE-ER-SU" else rate_flags_str = "Unknown" end return rate_flags_str end function getRate(rate_flags, rate) local rate_str = "" -- Lgeacy rates if rate_flags == 0x00 then if rate == 55 then rate_str = "Data rate: 5.5 Mbps" else rate_str = "Data rate: " .. rate .. " Mbps" end else rate_str = "MCS Index" .. rate end return rate_str end -- This function will dissect the packet function nordic_raw_80211.dissector(buffer, pinfo, tree) -- Dissect the first 6 bytes (Raw RX custom header) local payload = buffer(6):tvb() local subtree = tree:add(nordic_raw_80211, buffer(), "Nordic Raw 802.11 Dissector") subtree:add(buffer(0, 2), "Frequency: " .. buffer(0, 2):le_uint()) -- Convert mBm to dBm and display as signed char local mBm = buffer(2, 2):le_int() local dBm = toSignedChar(mBm / 100) subtree:add(buffer(2, 2), "Signal (dBm): " .. dBm) subtree:add(buffer(4, 1), "Rate Flags: " .. getRateFlags(buffer(4, 1):uint())) subtree:add(buffer(5, 1), getRate(buffer(4, 1):uint(), buffer(5, 1):uint())) local wlan_dissector_name = "wlan" local wlan_dissector = Dissector.get(wlan_dissector_name) if wlan_dissector == nil then print("Error: No dissector found for " .. wlan_dissector_name) return end -- Call IEEE 802.11 dissector wlan_dissector:call(payload, pinfo, tree) end -- Register the dissector local netcapture_udp_port = 4242 local udp_port = DissectorTable.get("udp.port") udp_port:add(netcapture_udp_port, nordic_raw_80211)
Copy the Lua script to the Wireshark plugin directory.
The plugin directory can be found in the Wireshark preferences.
Open Wireshark and either start capturing packets or open a capture file.
The UDP payload for port
4242is now dissected as follows:Nordic Raw 802.11 header
IEEE 802.11 packet
See the reference image below:
UDP payload
Dependencies
This sample uses the following nRF Connect SDK library:
